
Al-Azawi study experimentally on natural convection heat transfer from longitudinal trapezoidal fins array heat sink subjected to the influence of orientation. Effects of fin length and fin spacing were observed for wide range of Rayleigh numbers.
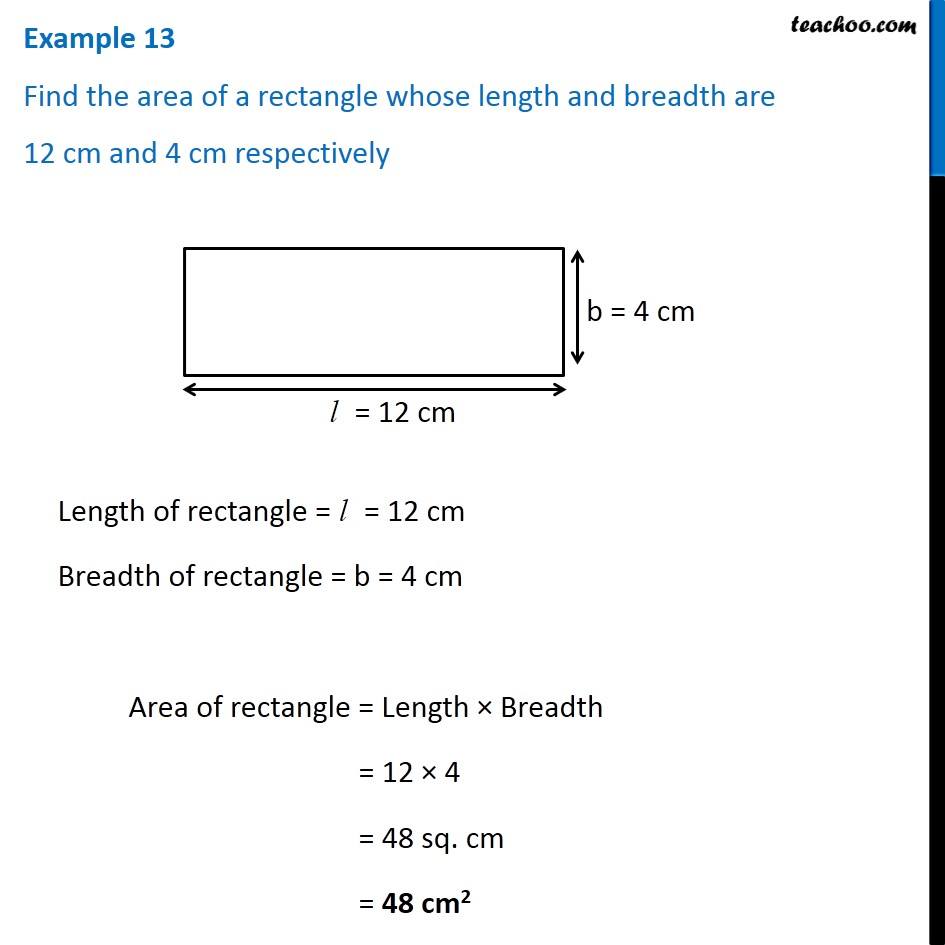
#SURFACE AREA OF RECTANGLE NUMBER OF FINS FREE#
Nada investigated experimentally the free convection heat transfer and flow characteristics of heated rectangular fin arrays in enclosures. conducted numerical study to investigate the natural convection from horizontally placed rectangular thick fin arrays with short lengths& observed that the free convection heat transfer coefficient increases with the increasing differences in temperature and fin spacing whereas decreases with increase in fin length. analyzed natural convection from rectangular and vertical finned plates numerically in order to optimize the fin configuration. Yüncü and Anbar conducted an experimental study of natural convection heat transfer from horizontally placed rectangular fin arrays&found that the natural heat transfer rate reaches to a maximum value as a function of fin height and fin spacing for a given base-to-ambient temperature.

performed an experimental study on heat transfer from vertically placed fin arrays produced from an aluminum alloy & found that for different configurations the maximum heat transfer rate from the fin arrays was obtained at the fin spacing value of 10 mm. Study natural convection heat transfer from four different fin array configurations with three base types and heat transfer coefficients were calculated& concluded that fin height, fin spacing and base orientation have significant effect on rate of heat transfer from fin arrays.Leung and Probert carried out experimental study on the effects ofįin spacing and fin height for a limited number of both vertically and horizontally oriented fin arrays configurations &observed that optimum fin spacing was within 9.0 – 9.5 mm range for a fin array that has 150 mm length.Leung et al. Investigated natural convection heat transfer from vertically oriented rectangular fin arrays experimentally & found that fin spacing is the most important variable for maximum natural heat transfer rate.Starner and McManus Yazcolu performed an experimental study on steady state natural convection heat transfer from vertical rectangular fins & found that the rate of heat transfer from fin arrays depends on the geometric parameters and the base-to-ambient temperature differences.Güvenç Numerical studies were also done to find a convenient model for the phenomena. Natural convection from finned surfaces has been investigated in literature extensively both theoretically and experimentally. This usually unwanted by-product can decrease the performance of the systems since almost every engineering system is designed to work in a certain temperature limit.Using fins is one of the cheapest and easiest ways to dissipate unwanted heat. Heat is generated as a by-product in many engineering applications.
.png)
Keywords: Natural convection, Extended surfaces, Optimal fin spacing, CFD The results are compared with those obtained experimentally & numerically for rectangular fins with same surface area, fin tip thickness & base plate dimensions. The heat inputs ranging from 25 W to 125 W has been supplied for fin configuration, and hence, the base and the ambient temperatures are measured in order to evaluate the heat transfer rate from fin arrays. The effect of heat loads on base-to-ambient temperature difference and on the heat transfer performance of trapezoidal fin arrays for the optimum fin separation values has been studied with the help of simulation models. This paper concerned with Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study of the steady-state natural convection heat transfer from vertical trapezoidal fins extending perpendicularly from vertical rectangular base. scholar, (Heat Power &Thermal), LNCT, Bhopal, IndiaĪssociate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, LNCT, Bhopal, India Comparative Study of Performance of Trapezoidal and Rectangular Fins on a Vertical Base Under Free Convection Heat Transfer


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
